Let's learn to automate tasks and operations within the Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment using python and boto3 which is the library of python to interact with AWS.
Requirements:
Pycharm
Boto3
Boto3 is a Python library or software development kit (SDK) that provides an interface to interact with Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Boto3 Installation
Before installing Boto3, install Python 3.8 or later; support for Python 3.6 and earlier is deprecated.
Before using Boto3, you need to set up authentication credentials for your AWS account using either the IAM Console or the AWS CLI.
If you have the AWS CLI installed, then you can use the aws configure command to configure your credentials file.
pip install boto3
aws configure
To configure we need credentials (Access id and secret key) we can get it from IAM user. We can use root user credentials but it is not recommended. So lets go with IAM User.
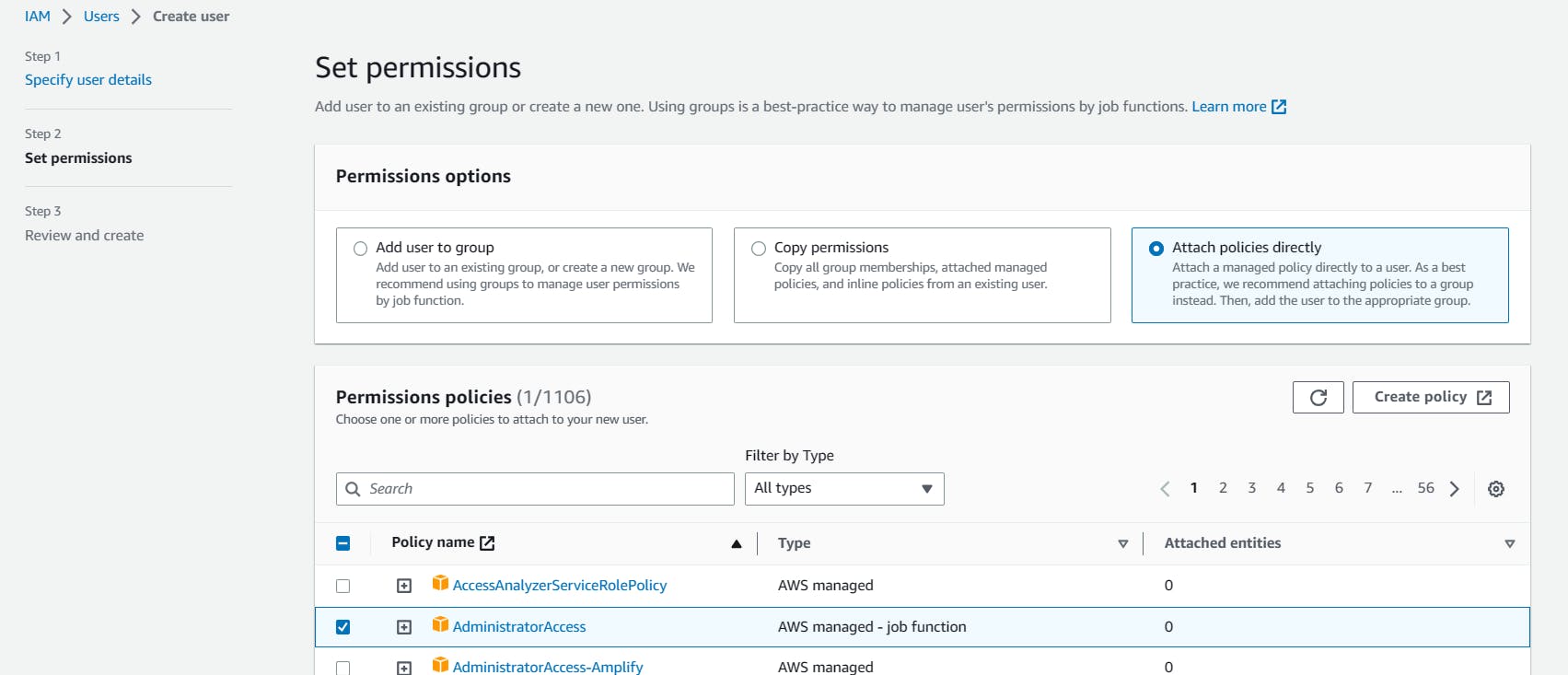
Create IAM User
Give Administrative access policy.

Run this python file.
import boto3
def create_user(username):
iam = boto3.client('iam')
response = iam.create_user(UserName=username)
print(response)
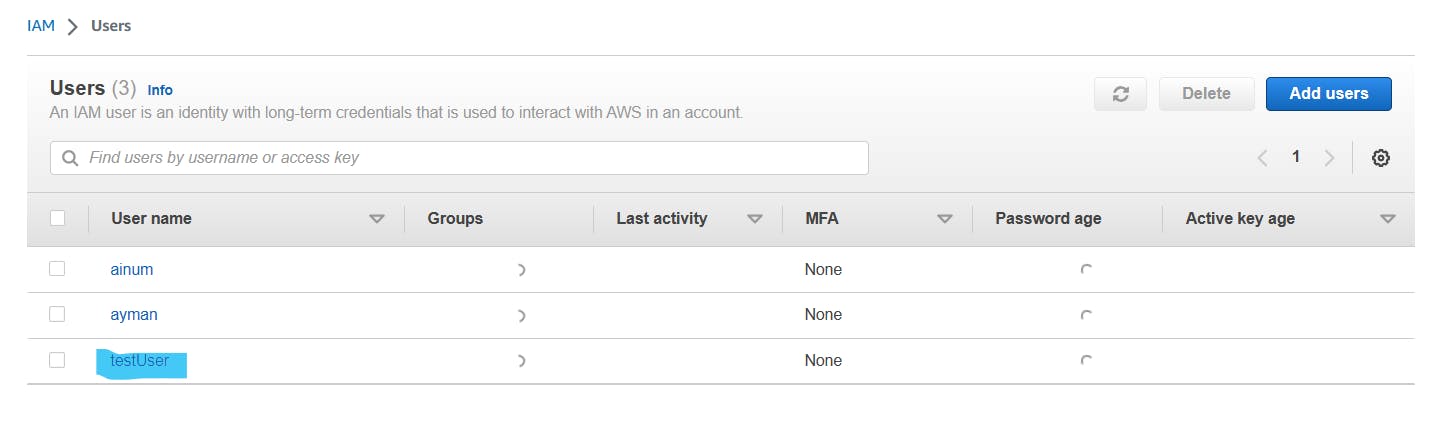
create_user('testUser')
creates an IAM client using boto3.client('iam')
creates an IAM client
iam.create_user(UserName=username) line sends a request to the IAM service to create a new user with the specified username. The response from the server is stored in the response variable.
create_user('testUser') line invokes the create_user function, passing in the string 'testUser' as the username argument.

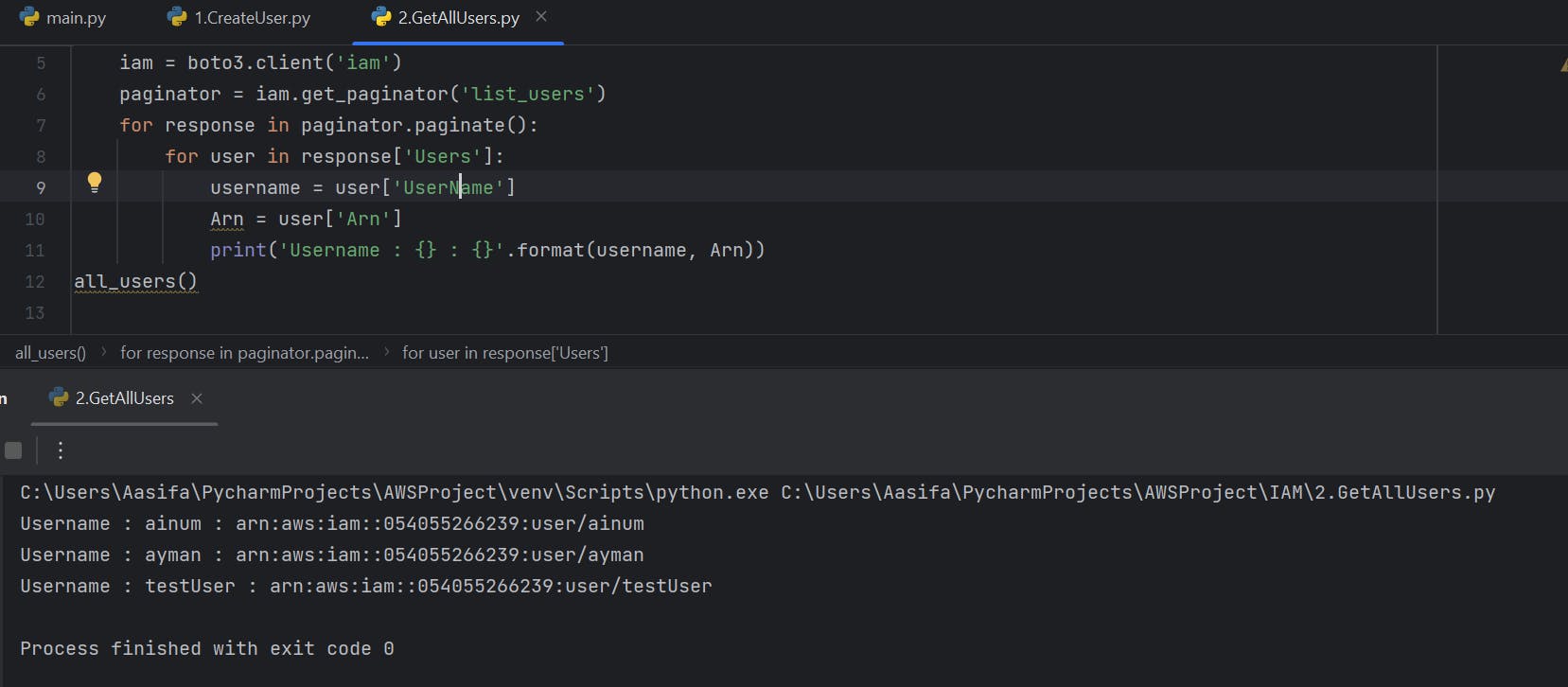
Getting All Users from AWS with Python
Now Let's retrieve all the users from IAM services.
Paginator :
AWS services often return large sets of data that cannot be retrieved in a single response due to limitations on response size or performance considerations. Instead, the data is divided into multiple pages or chunks, and the paginator assists in fetching these pages iteratively.
import boto3
def all_users():
iam = boto3.client('iam')
paginator = iam.get_paginator('list_users')
for response in paginator.paginate():
for user in response['Users']:
username=user['Username']
Arn=user['Arn']
print('Username : {} : {}'.format(username, Arn)
all_users()
for response in paginator.paginate()::
This line initiates a loop that iterates over the paginated responses obtained by calling paginator.paginate(). It fetches one response at a time, allowing you to access the data contained within.
for user in response['Users']:
Within each response, this line starts another loop that iterates over the list of users stored in the 'Users' key of the response. It allows you to access each user's information individually.
username = user['Username']:
For each user, this line retrieves the value of the 'Username' key from the user dictionary and assigns it to the variable username. It captures the username of the current user being processed.
Arn = user['Arn']:
Similarly, this line retrieves the value of the 'Arn' key from the user dictionary and assigns it to the variable Arn. It captures the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the current user being processed.