Table of contents
- RDS
- RDS - A fully managed service by AWS
- What customer needs to manage?
- Different relational database options available in RDS
- RDS Limits
- Instance storage
- Concept of Multi-AZ
- When Multi-AZ RDS failover triggers? (when it will move to standby?)
- The difference between Read Replicas and Multi-AZ
- Hands-On
- Connecting using SQL electron
- Connecting using EC2 instance
RDS
RDS (Relational Database Service) is a managed service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). Generally, Relational Database organizes data into one or more tables with a predefined structure, where each table consists of rows and columns. The data in these tables is related to each other using keys, which establish a relationship between the tables.
Example : Banking systems: Banking systems use relational databases to store customer information, account balances, transaction histories, and other financial data. For example, a bank might have tables for customers, accounts, transactions, and ATM locations, with relationships between the tables to track money flows and user activity.
RDS - A fully managed service by AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) manages several aspects of RDS to make it easier for customers to set up, operate, and scale their databases in the cloud. Such as,
Infrastructure:
AWS manages the underlying infrastructure, including servers, storage, networking, and security, so that customers don't have to worry about managing these components themselves.
Software updates and patching:
Patching in RDS terms, patching refers to updating the database software to the latest version that includes bug fixes, security patches, and other improvements. AWS automatically applies software updates and security patches to the RDS instances, ensuring that customers always have access to the latest version of their database software.
Backup and recovery:
AWS automatically performs backups of the RDS database instances according to customer-defined backup policies and also enables customers to perform manual backups and point-in-time restores as needed.
High availability and failover:
AWS provides multiple availability zones for RDS instances, which enables automatic failover in case of a hardware or software failure, ensuring that customers have continuous access to their databases.
Monitoring and metrics:
AWS provides a range of monitoring and metrics tools for RDS, including CloudWatch and Performance Insights, which enable customers to monitor their database performance and troubleshoot issues.
Security:
AWS provides a range of security features for RDS, including network isolation, encryption, and access control, to ensure that customer data is secure and protected.
What customer needs to manage?
Managing database settings
Creating a relational database schema
Database performance tuning (database performance tuning in RDS is a continuous process that involves monitoring, testing, and adjusting various parameters to achieve the best possible performance for the application. )
Different relational database options available in RDS
MS SQL Server
My SQL
Oracle
AWS Aurora (high throughput)
PostgreSQL (stable and reliable )
Maria DB (MySQL compatible )
RDS Limits
1. Upto 40 DB instances you can create per account
10/40 can be Oracle or MS- SQL server under was a license
40/40 can be all databases under BYOL (bring your own license )
Instance storage
Generally, databases will be created in EC2 but we don't have access to ec2. Only have access to a database that is created on ec2. And the rrot volume of the ec2 instance is EBS volume.
Storage options
General purpose
Provisioned IOPS
Concept of Multi-AZ
Inorder to provide fault tolerance and high availability.
You need to select the Multi-AZ option if you want to create a standby/replica of database. Multi-AZ helps when you plan a disaster recovery for an entire AZ going down. If you plan against an entire AWS Region going down, you should use backups and replication across AWS Regions.
When you are creating a database you can either choose standalone or standby (replica of the database in case of failure). Standby will be made in another availability zone of the same region.
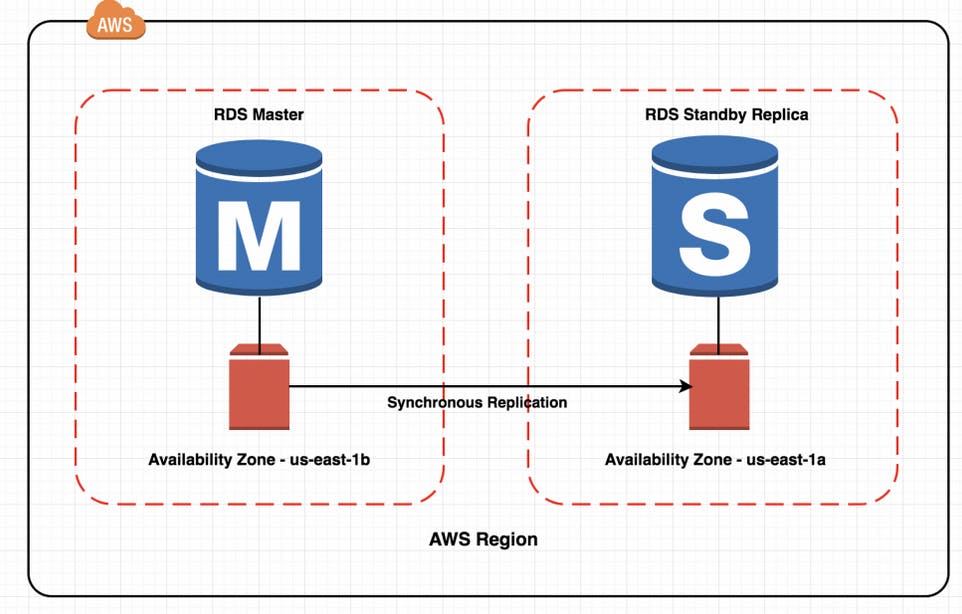
You can see above that we have one Master database in one AZ. If we go by standby , another replica of the database will be created in another AZ of the same region. Whatever changes done in the master will also synchronously be reflected in the replica. If the Master database fails, then replica/standby becomes Master.
This is called Automatic failover recovery.
--> You can select multi-AZ option when you are creating a database.
--> You cannot create a standby in one particular AZ, AWS will automatically creates a standby in AZ.
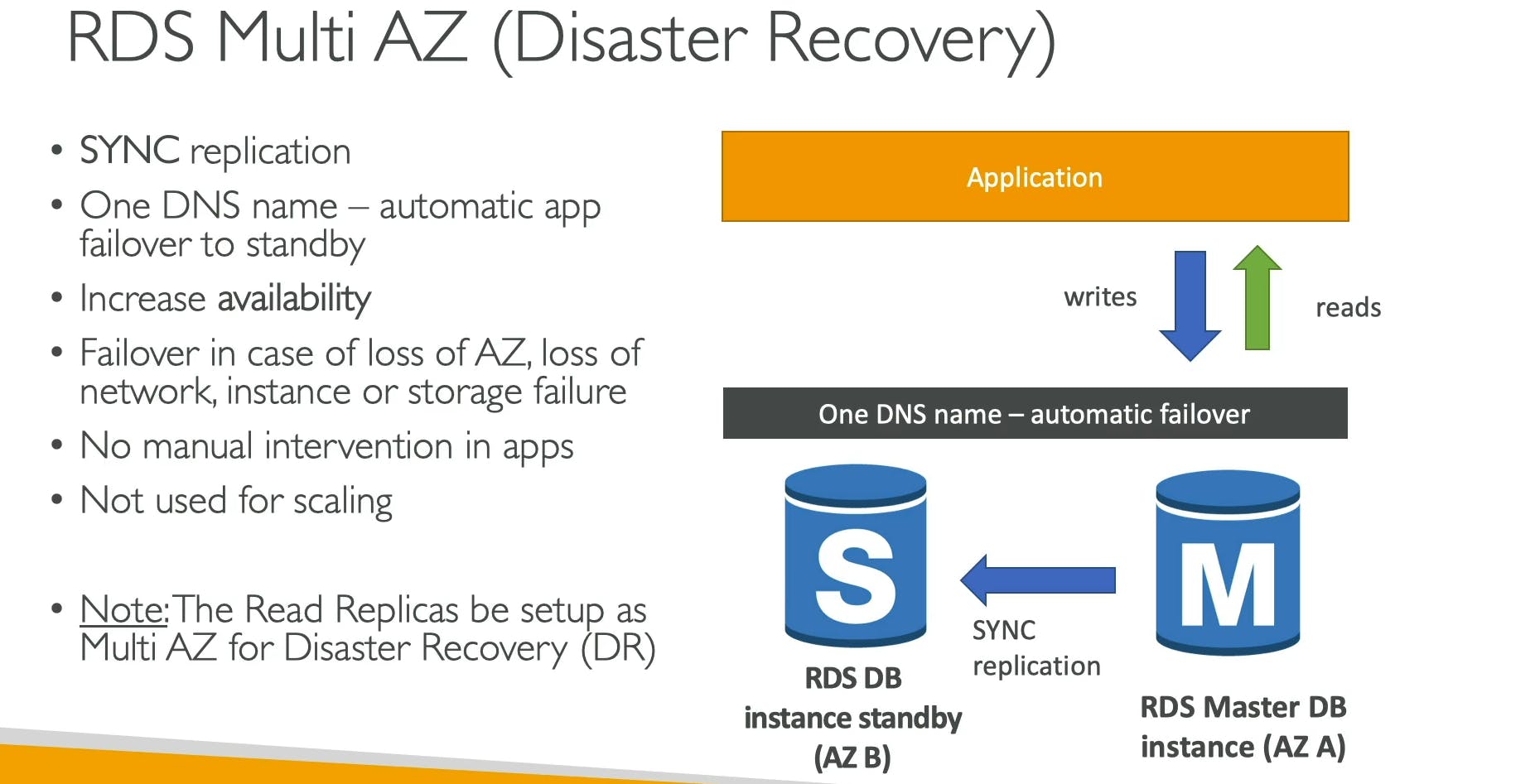
When Multi-AZ RDS failover triggers? (when it will move to standby?)
When your primary db instance fails.
When AZ fails
loss of network connection
EBS of primary instance is fails
Patching the OS of the DB instance.
Manual failure of primary ( when you are doing maintenance of primary)
The difference between Read Replicas and Multi-AZ
Read replicas and Multi-AZ (Availability Zone) are two different mechanisms used in database replication to improve data availability and durability in Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment.
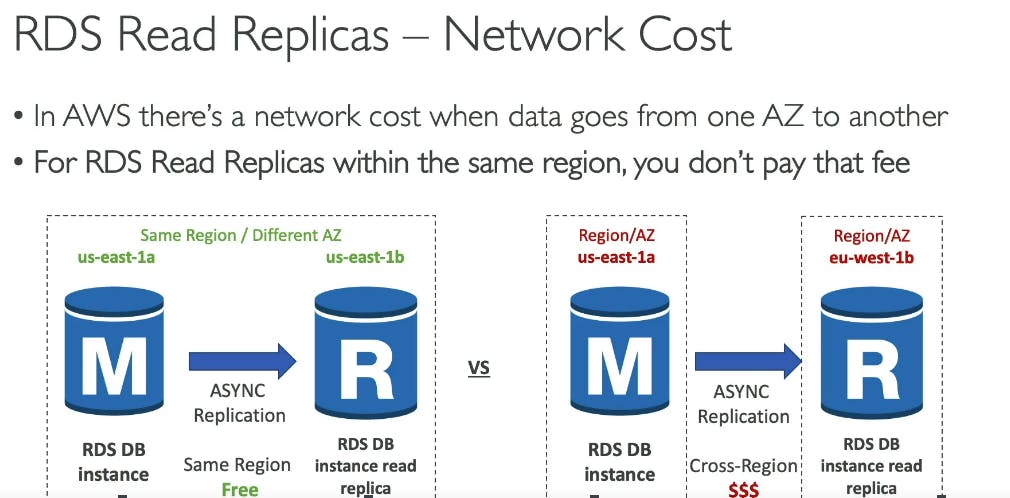
Read Replicas: These are the copies of the primary database. Read replicas are called "read" replicas because their primary purpose is to handle read requests from the application, while the primary database handles write requests. changes will be asynchronously replicated. With asynchronous replication, changes made to the primary database are asynchronously propagated to the read replicas. This means that the primary database does not wait for confirmation that the changes have been made to the read replicas before proceeding with the next operation. However, read replicas are not designed for failover or disaster recovery, and they do not provide automatic failover or recovery.

-->Multi-AZ is a feature that provides high availability for the primary database by automatically replicating the data to a standby database in a different Availability Zone (AZ) within the same region. Multi-AZ is designed to provide automatic failover and data durability, ensuring that your database remains available even if the primary database becomes unavailable.
Hands-On
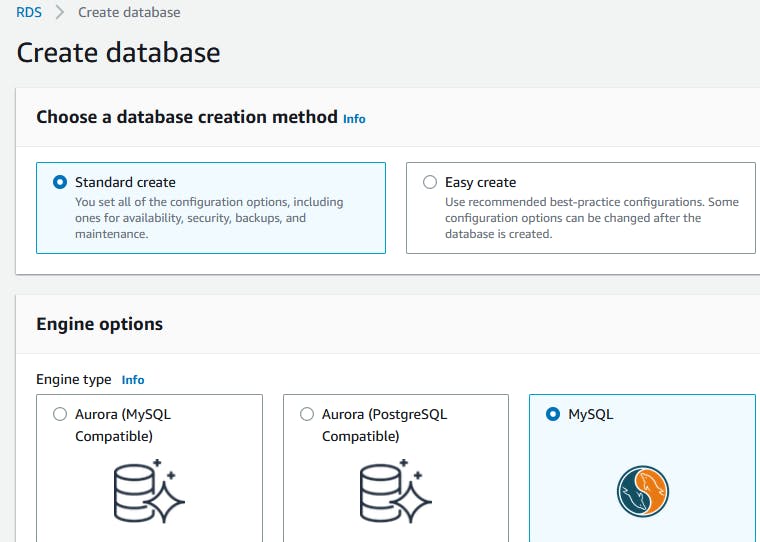
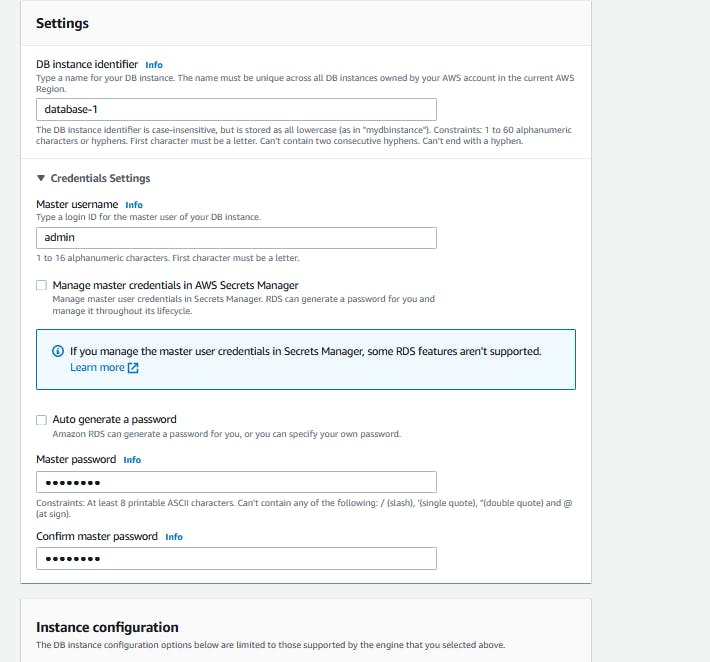

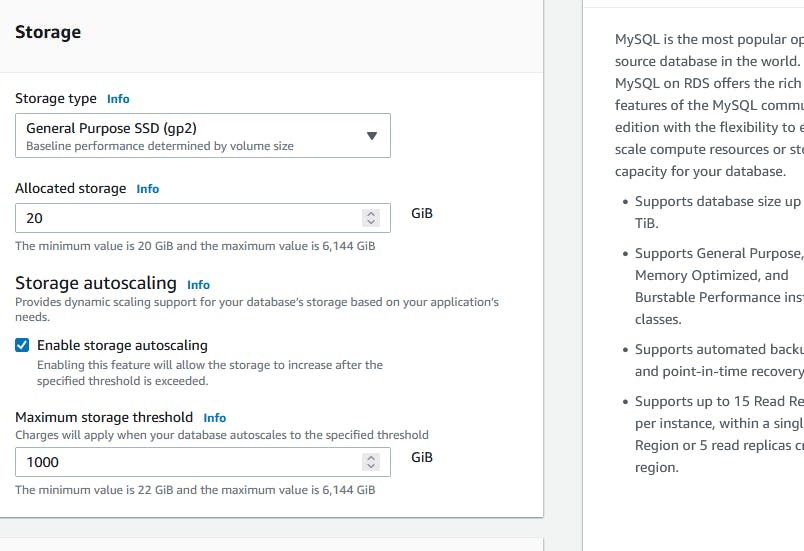
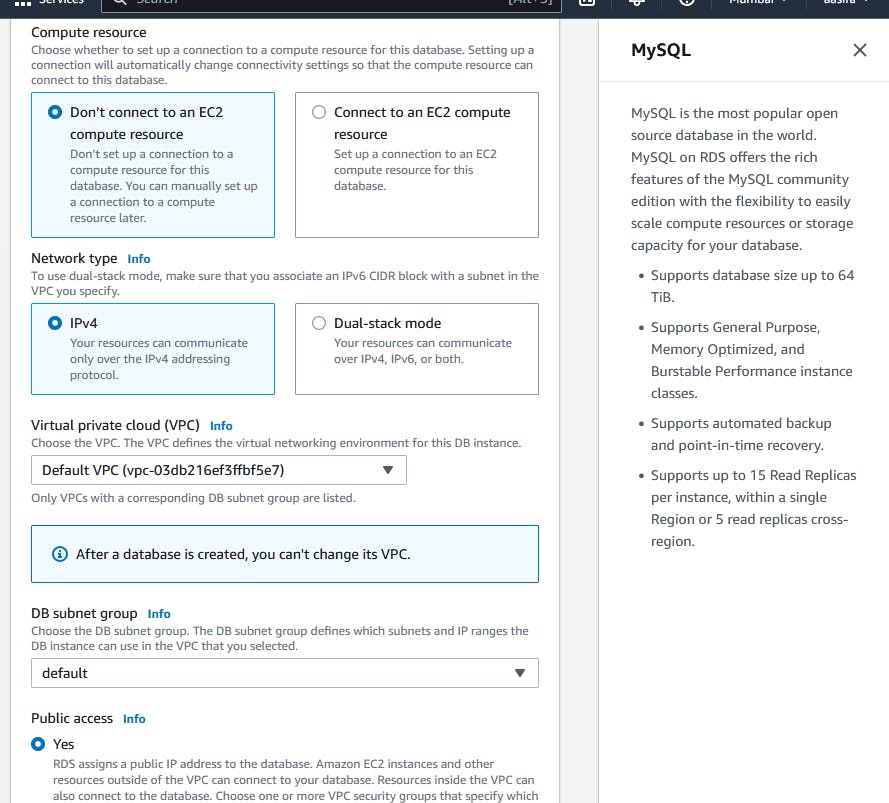
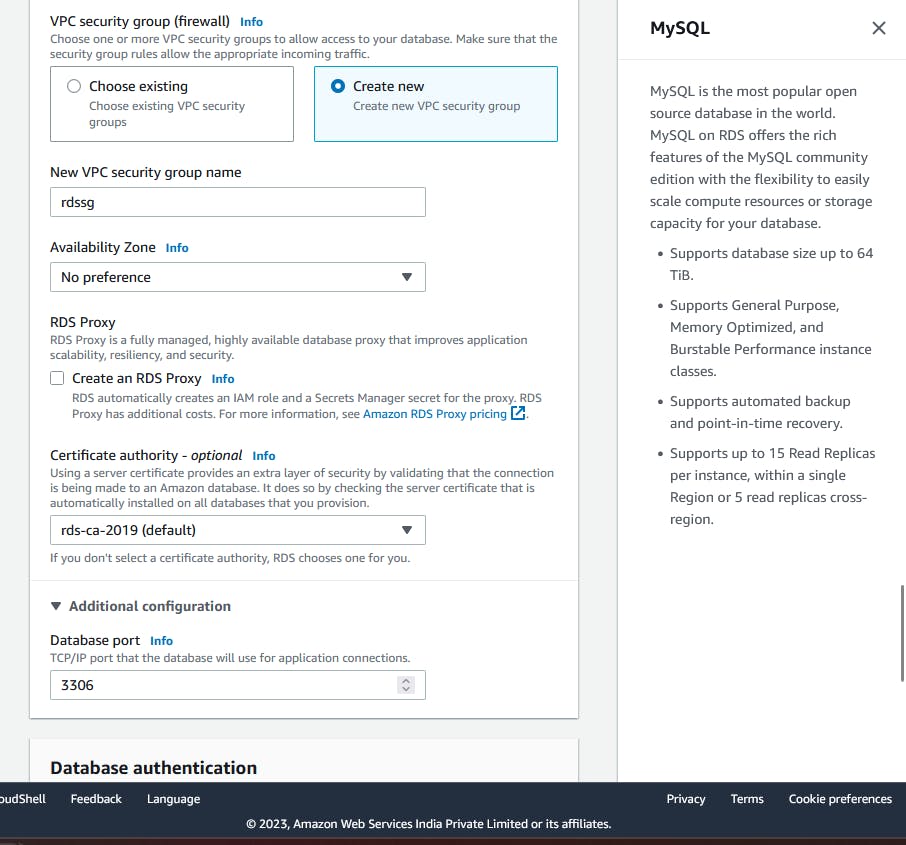
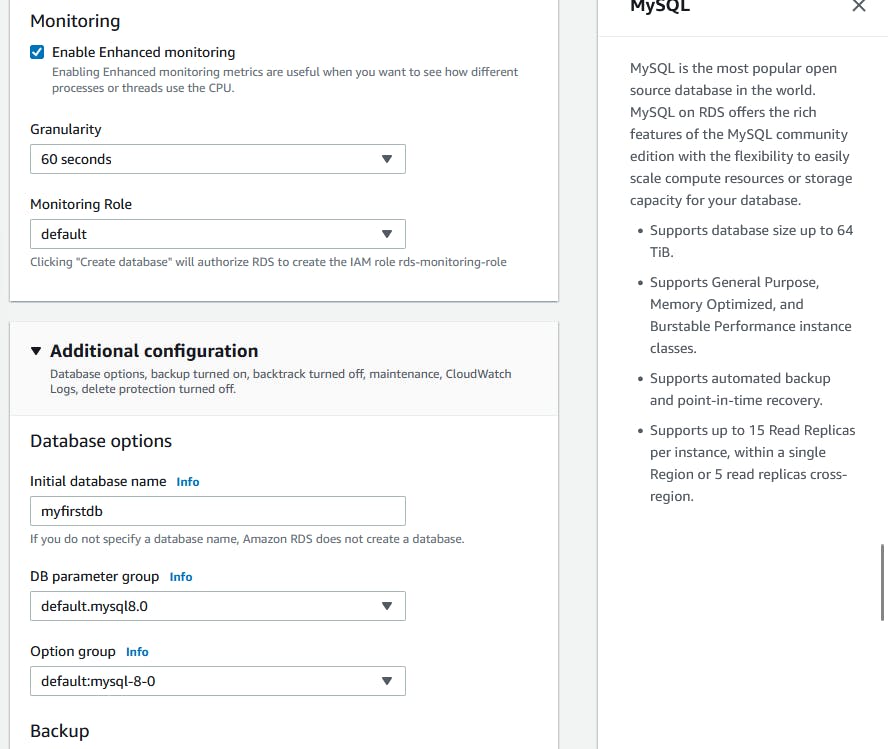

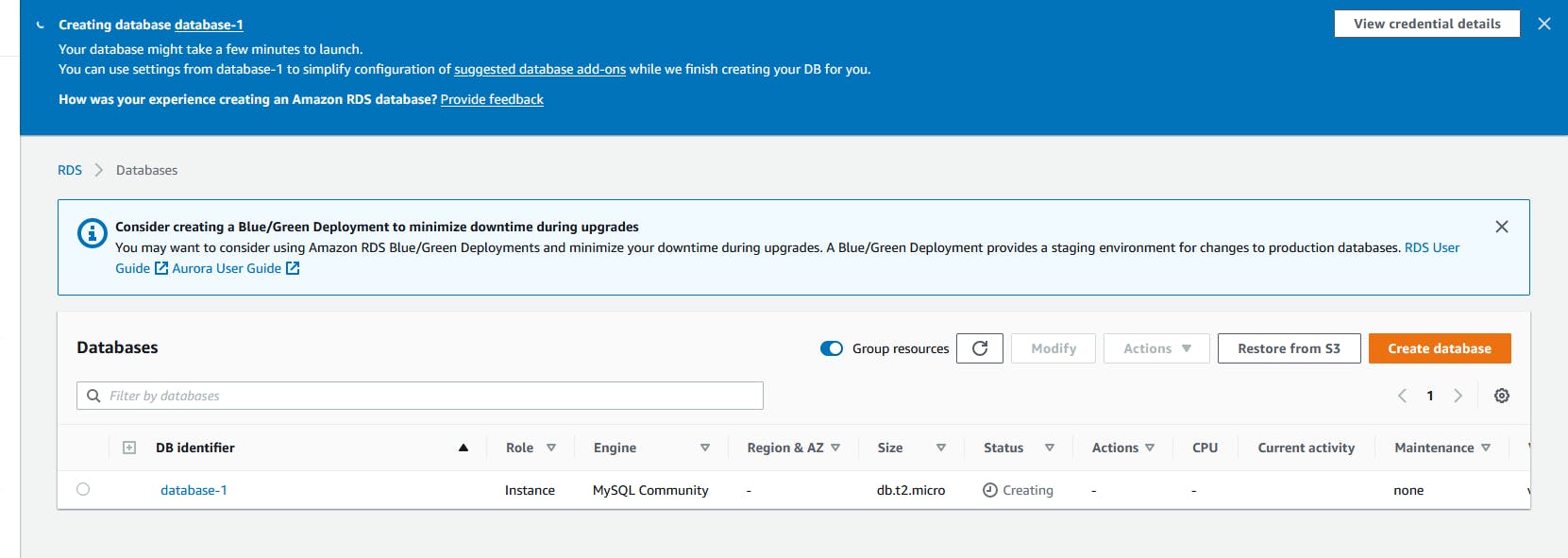

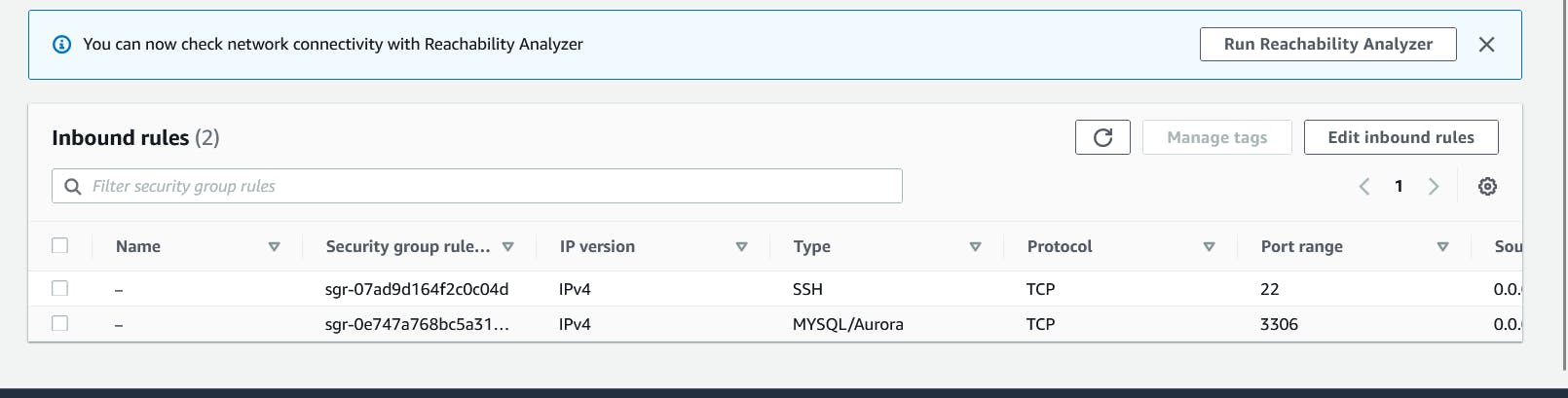
Change the SG to 3306 to anywhere.
Connecting using SQL electron
To connect the database i will use SQL electron.
Internet - Servers - Database Utils Downloads (softpedia.com)
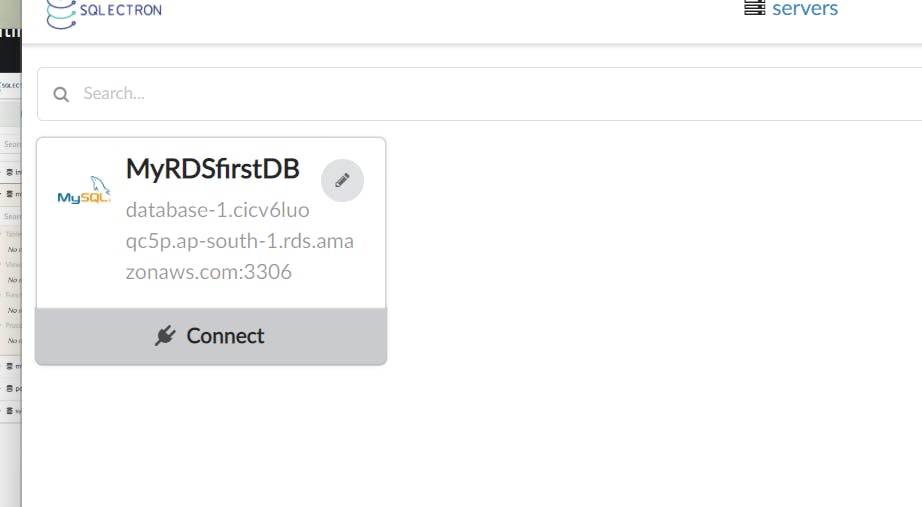
Copy endpoint URL of your database
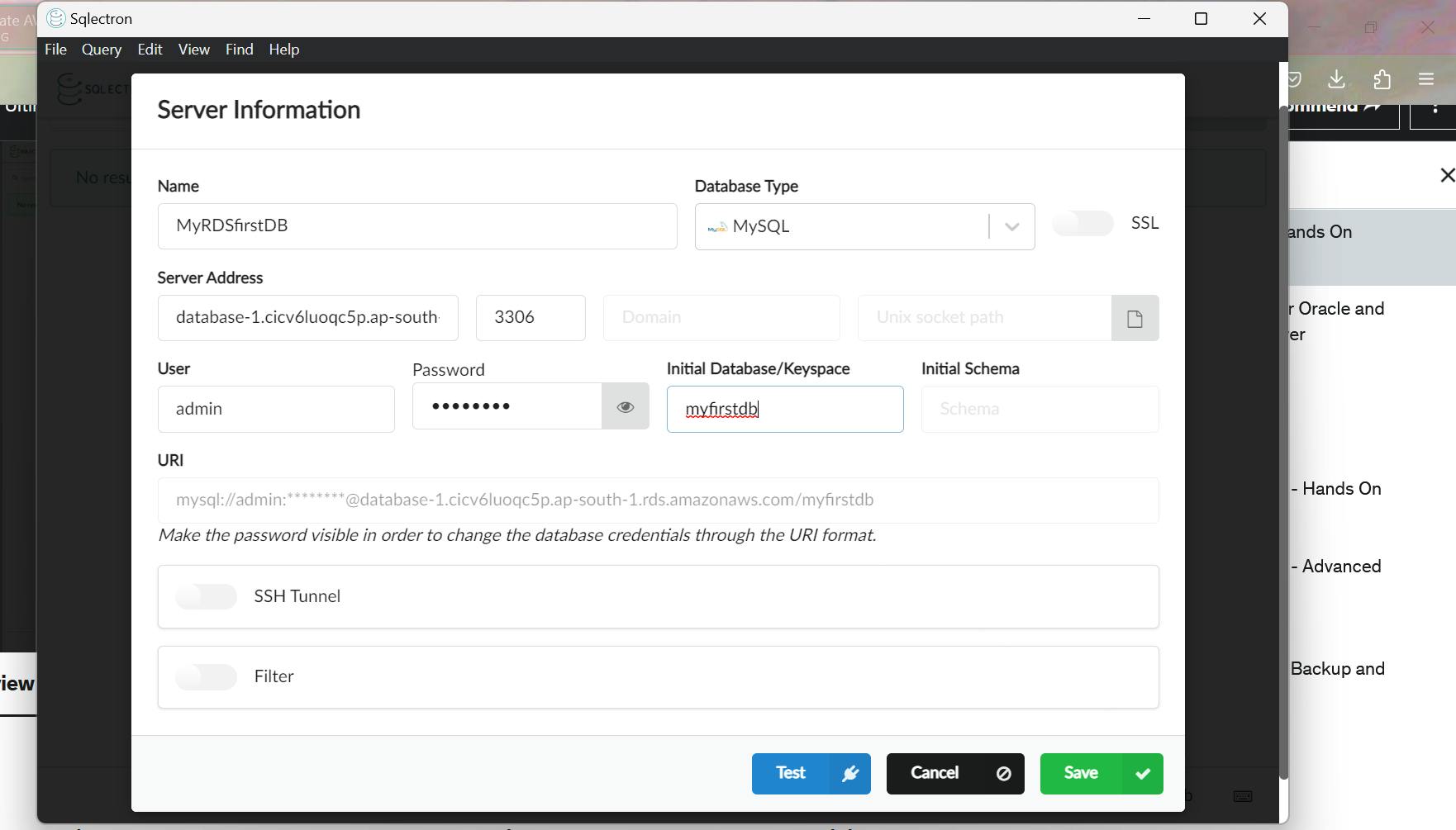
Click on Test
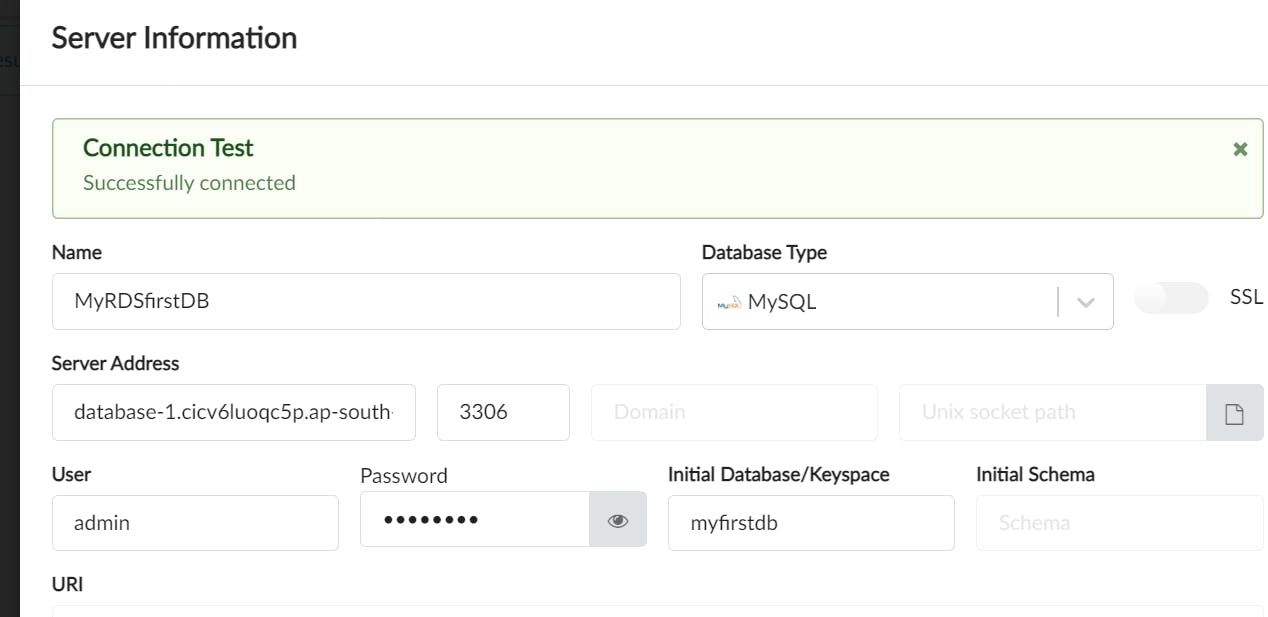
Save and connect to the db
Lets create a Table here 😄
CREATE TABLE students (
PersonID int,
LastName varchar(255),
FirstName varchar(255),
Address varchar(255),
City varchar(255)
);
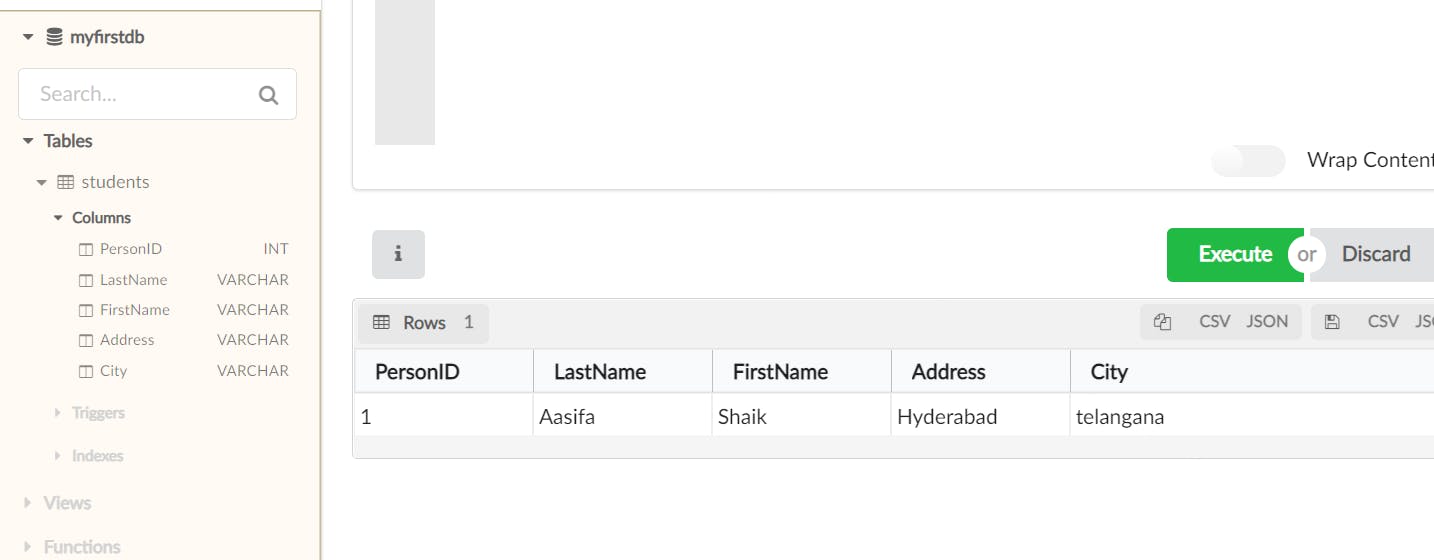
INSERT INTO students (PersonID, LastName, FirstName, Address, City)
VALUES (001,'Aasifa', 'Shaik', 'Hyderabad', 'telangana');
You can insert the data and perform other operations
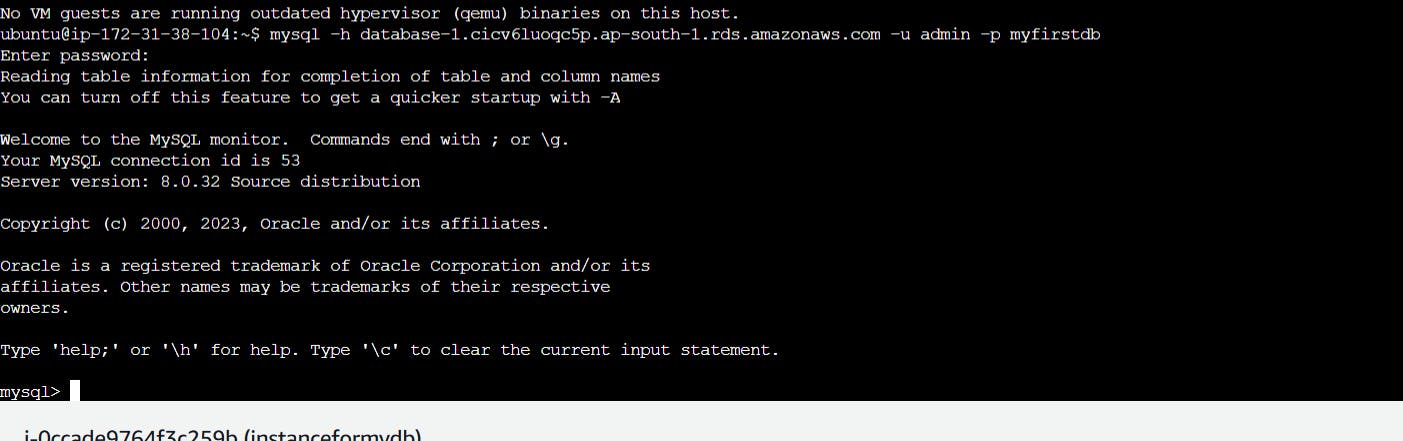
Connecting using EC2 instance
While creating select SG that we created for RDS database.

Give following commands to update, install MySQL and to connect to the server.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install mysql-client-core-8.0
#give username as admin, and databasename
mysql -h database-1.cicv6luoqc5p.ap-south-1.rds.amazonaws.com -u admin -p myfirstdb
Now our RDS DB is successfully connected and you can access it via EC2😃😌👍
I hope you learnt about RDS. Follow more for such articles. Thank you for your time 🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈🌈