Introduction
Openshift is RedHat's open-source container application platform for developing and hosting enterprise-grade applications.
It is a Red Hat's Platform as a Service offering. Once deployed Openshift takes care of managing the underlying infrastructure components thereby enabling the developers to do what they do best -Code.
Kubernetes Vs Openshift
🌷Kubernetes and OpenShift are both popular container orchestration platforms used in the world of cloud-native application deployment and management.
🌷While Kubernetes is an open-source project developed by Google, OpenShift is a Kubernetes-based container platform developed by Red Hat.
🌷Developed by Red Hat, OpenShift is a Kubernetes-based platform. It extends Kubernetes with additional features and tools.
🌷There are multiple versions of OpenShift, including OpenShift Container Platform (for enterprises), OpenShift Online (hosted and managed by Red Hat), and OpenShift Origin (the open-source, community-driven version).
🌷OpenShift builds on top of Kubernetes and provides additional features out of the box, such as developer and operational tools, integrated CI/CD pipelines, monitoring, and logging. These features are tightly integrated into the platform, simplifying the deployment and management process.
Openshift Components and Architecture
🌷Openshift leverages Kubernetes underneath as the primary infrastructure component.
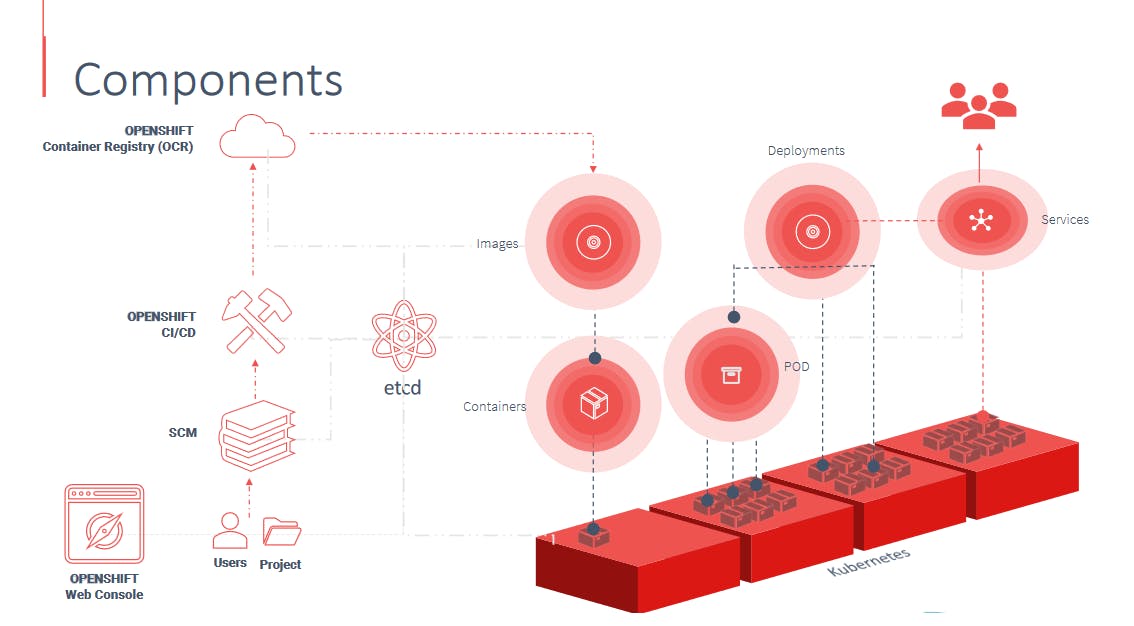
🌷Kubernetes you can deploy applications in the form of containers such as Docker
containers. Containers are created from images of applications. But where do these Docker images come from? You may configure Openshift to pull these images from a public Docker repository or registry like Docker Hub. Alternatively you may use the Openshift container registry that comes built in with Openshift Origin.
🌷A collection of one or more containers together for a pod and multiple pods form a deployment. We use services to expose the deployments to other applications or to the external world. Kubernetes constructs that Openshift leverages to manage all of these with ease.
🌷Openshift comes with a built-in web console that developers can access to browse and manage their applications.
🌷This web console can only be accessed by users which are managed by Openshifts authentication and authorization mechanisms.
🌷At the heart of Openshift lies the ETCD Key value store that stores information about various components.
Build
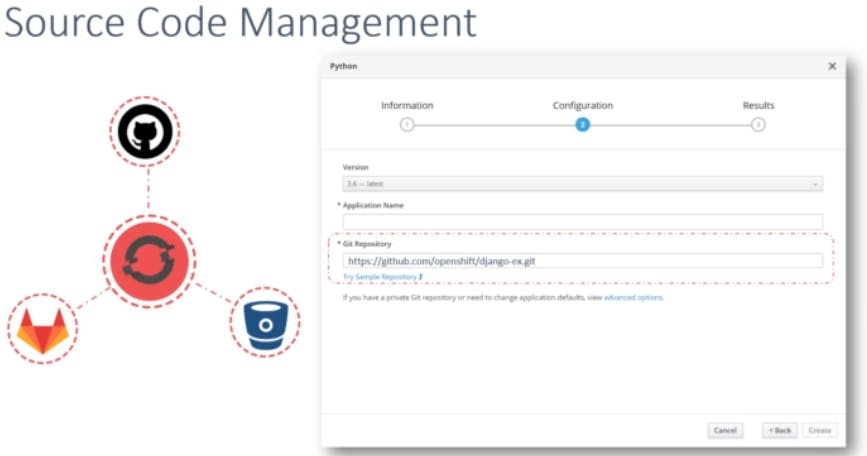
Openshift has built in integration to source code management tools hosted internally or externally such as GitHub, GitLab and Bitbucket etc.. So you must have your application code uploaded to a source code repository in order to deploy it on openshift.
When you try to add the application to a project in Openshift specify the location of the source code repository in the Git Repository field.
In this case, we are using a sample application hosted on a GitHub code repository.
When you add an application to a project Openshift automatically creates a build job for the application using the URL in the code repository specified in the above step.

When run, the Build downloads a copy of the code from the code repository and builds the code using a predefined Build configuration into a Docker image.The Docker image is then pushed to the built-in Docker registry.
Deployment
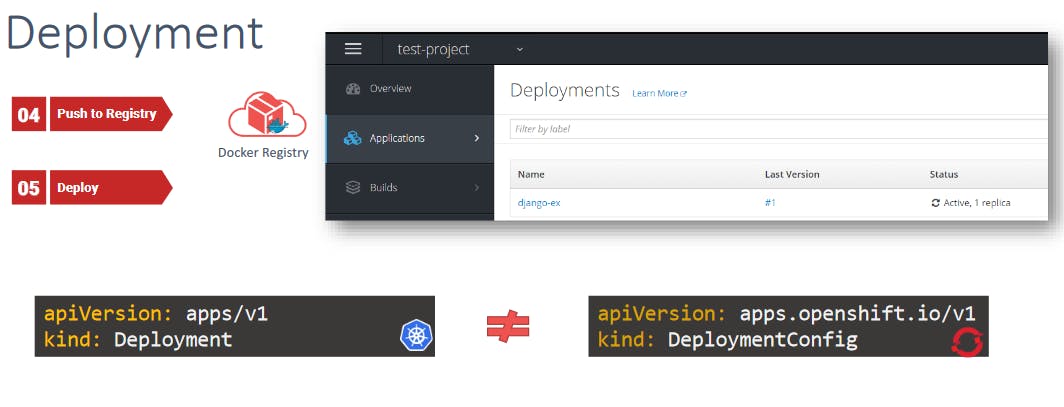
Along with creating a build, Openshift also creates a deployment automatically. On a successful build, the deployment deploys the application using the image from the internal Docker registry to the built-in Kubernetes cluster making the application available to the end users. Deployments in Openshift are similar to the concept of deployments in Kubernetes if you are familiar with it. But they are really not the same. By default, Openshift creates a deployment using a deployment config object which is part of the Openshift API for Kubernetes. As opposed to the deployment object in Kubernetes, which is part of the Kubernetes native API.
🌷 Let's learn more about open shift in upcoming blogs. Thank you for your time🌷